How to Read a Cap Table? Usages, Key Terms, and More
A cap table is relatively simple to comprehend. It’s a table typically made on a spreadsheet during the inception of startups. It lists all the company’s shareholders and shows who owns what, how much they own, and how much value is allocated to the shares they own.
Cap tables are crucial for several reasons; however, one of the most important factors is that they help investors understand what they’re buying while also assisting all shareholders in keeping track of their stake as the firm raises more capital.
This article will explain a cap table, its different elements, and how to read one.
What is a Cap Table?
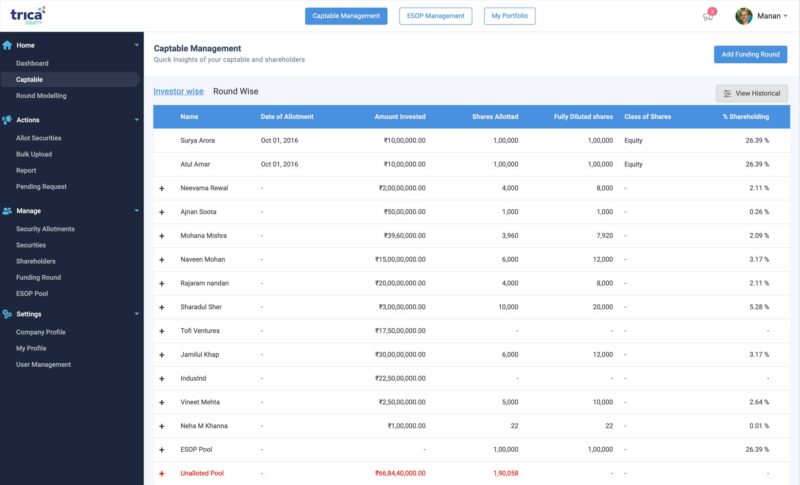
The cap table is a detailed analysis of a company’s equity held by its shareholders. Cap tables comprise a company’s equity capitalization, including common equity shares, preferred equity shares, warrants, and convertible equity.
Usages of Cap Table
The following are some of the use cases of a cap table:
1. Raising funds
Investors are interested in knowing how the company’s ownership is constituted and the changes in past financing rounds while negotiating for new capital. Investors may have queries that the cap table can answer.
New investors, for example, will want to know how their investments may affect other investors. In addition, they wish to prevent any possible legal issues that could cause them to clash with other investors. Finally, investors also want to know where they rank in terms of liquidity.
2. Hiring employees
Most companies are becoming more open about cap tables with their employees—this aids in retaining high-performing personnel and motivates them to continue serving the organization.
Corporate executives want to know how much money they’ll get from their ownership portion if the company sells or is liquidated. Even when the company is in financial trouble, transparent and organized companies have a better chance of retaining their staff.
3. Tax and regulation compliance
Cap tables are used as a formal legal record of stock ownership and by tax authorities to determine if the company, its employees, and its investors are paying the required taxes.
The company or its employees may end up paying more taxes than they need to if the cap tables are not updated regularly. Conversely, if the company filed lesser taxes than was required, it might face steep penalties.
4. Selling the company
When a firm decides to sell its business to a third party, the proceeds are distributed among the shareholders. The cap table shows how much and in what sequence each stakeholder receives from the proceeds.
Any disagreements or litigation that may develop as a result of the funds’ distribution can be avoided with an updated cap table.
Key Terms Used in a Cap Table
To become a successful investor, every investor needs to comprehend the critical terms used in the cap table:
Security Types
Common stock: Shares of common stock reflect a portion of a company’s ownership and indicate that each shareholder has specific profit rights and can vote in the company’s corporate activities.
Preferred stock: These are special classes of shares with special privileges and rights defined by the company’s charter.
Convertible preferred: These stock classes have the option to convert to common stock and be paid at the common stock rate at the same time.
Participating preferred: The preferred stock, in this case, has the right to be paid a multiple of the original price and can then be converted into common stock.
Non-participating preferred: The investor of this type of preferred stock has the option of being paid a multiple of the stock’s original price or converted into common shares while being available for distribution to common stockholders.
Stock options: It’s a contractual right to buy a certain number of shares at a specific price on a certain date or dates in the future. Stock options are usually granted under the provisions of a stock-option plan, in which a pre-approved pool of shares is set aside solely for options and restricted stock grants.
Warrants: They have the same options accessible to them, such as buying a certain number of shares at a certain price on a certain future date or dates.
Restricted stock: These stocks are granted up-front; however, up-front ownership is subject to certain restrictions.
Valuations
Pre-money valuation: This is a valuation given to a company before an investment is made in it. This valuation is frequently negotiated between the investors and the company’s management.
Post–money valuation: This valuation takes effect after a company is invested in, and the total of both becomes the company’s post-money valuation.
Price-per-share: This is calculated after the post-money stage by dividing the post-money valuation by the fully diluted shares.
Share Counts
Authorized shares: These shares are those that have been duly authorized for current or future references by the company’s board of directors.
Outstanding shares: These shares refer to the total number of shares that have been issued, excluding options that have not been exercised.
Fully diluted shares: This is the total number of shares after all granted options, restricted stock warrants, and issued shares have been considered. It also considers any unresolved issues or contingencies.
How Does A Cap Table Change?
During a company’s seed stage of investment, cap tables are typically kept basic. Changes to a cap table can occur as a result of the following events:
- Any transfer of stock from one person to another, such as another investor.
- Someone who is exercising their rights or exercising their warrants.
- The creation of a pool of options.
- The termination of any unused options, share awards, or expired warrants due to an employee’s departure from the organization.
Waterfall Analysis
In a liquidity situation, waterfall analysis shows how much each shareholder on the cap table will receive based on the amount of equity available.
Liquidity events are invariably unpredictable, and shareholders cannot know how or when they will occur. Therefore, waterfall analysis uses a set of assumptions to calculate the total percentage of proceeds distributed to shareholders if the company goes into liquidation.
Final Thoughts
One of the first things a startup company must do when preparing to obtain funding is set up a cap table. Investors must know how to read a cap table to ensure that their share of a company is correctly reflected. Hence, this way, investors can spot any irregularities and promptly alert the company to request corrections.
A well-managed cap table can open your doors to hundreds of potential investors that can help you take your business to the next level. trica has the right tool for you if you are looking for a cap table management software that offers all the perks mentioned above and many more additional features.
Talk to our experts at trica equity and book a demo today for a world-class experience with India’s finest cap table management software.
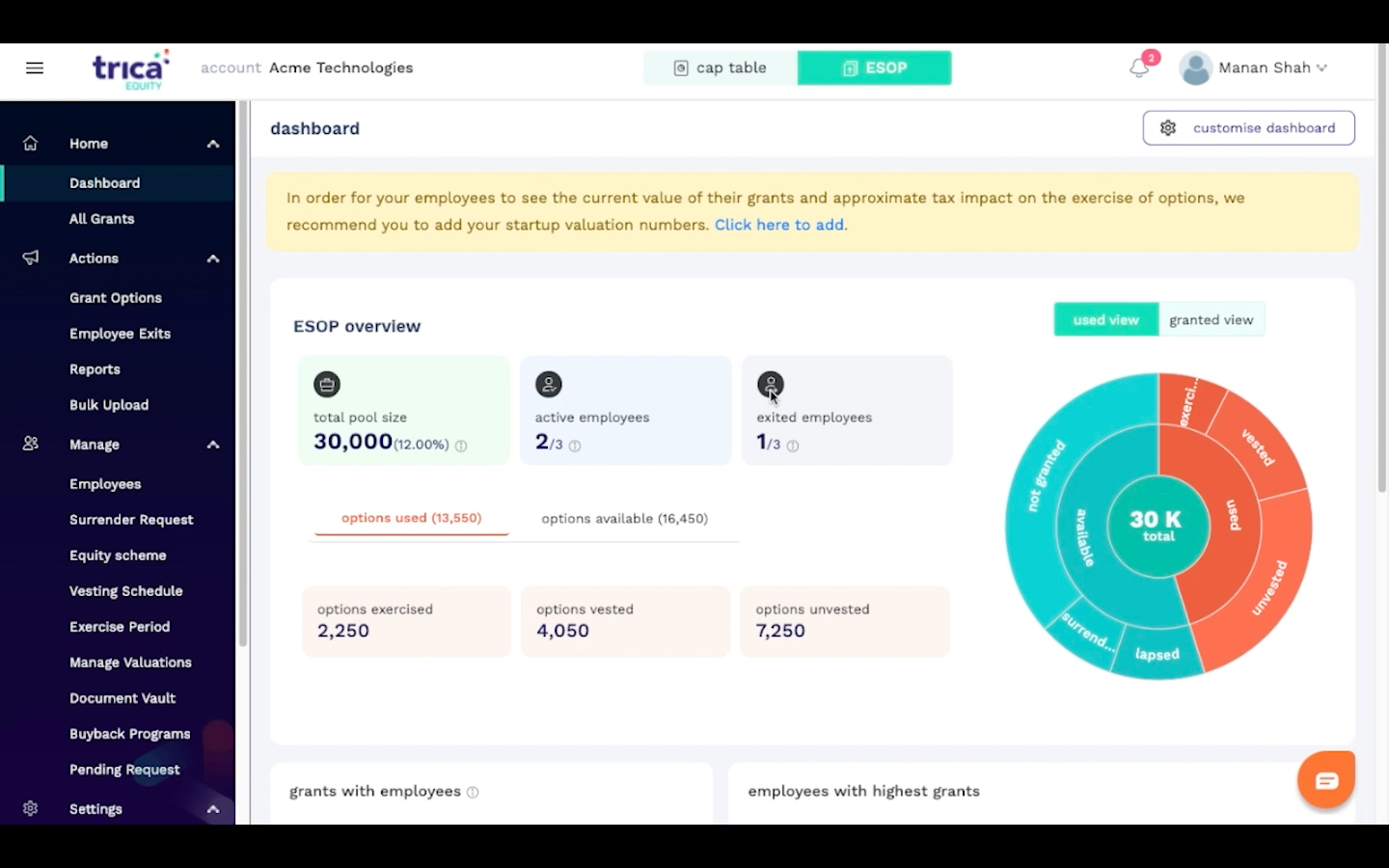
ESOP & CAP Table
Management simplified
Get started for free